Supplier Relationship Management
Quote from bsdinsight on 4 December 2023, 17:34
1. Key research findings
Chapter 1 presents the main observations and conclusions of our SRM study. Our findings are structured around six elements, namely:
- SRM objectives
- Typical SRM challenges
- Current maturity level
- Unique supplier capabilities
- Critical success factors
- Potential benefits
2. Towards world-class SRM
This chapter presents typical best practices to successfully establish and enhance
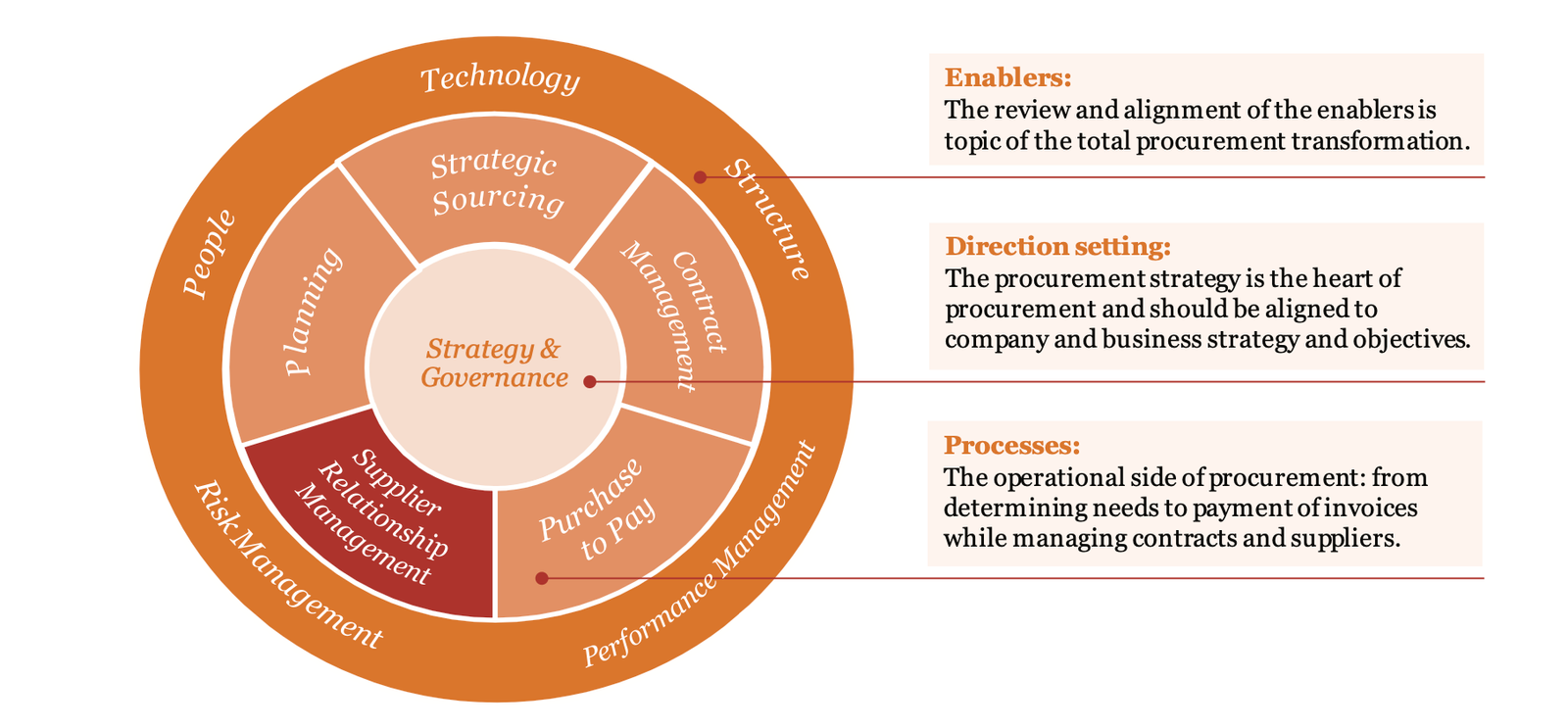
an SRM programme or to develop and manage partnerships. We will use the seven enablers from the Procurement Framework of PwC which are:
- Strategy & Governance: what does your organisation want to achieve with SRM and how are these objectives secured?
- Process: which activities does your organisation perform and how is SRM supported by a standard toolkit?
- Structure: how does your organisation structure SRM and which roles & responsibilities are established?
- People: which unique competencies does your organisation need to establish and manage SRM?
- Technology: which support systems does your organisation deploy?
- Performance Management: how does your organisation measure and improve partnership performance?
- Risk Management: how does your organisation identify and mitigate risks at key suppliers?
This chapter concludes with a short description of four key capabilities that, in our view, drive SRM value creation.
3. How to establish SRM
……
Xem và tải tài liệu ở đây
[dflip id="96666" ][/dflip]

1. Key research findings
Chapter 1 presents the main observations and conclusions of our SRM study. Our findings are structured around six elements, namely:
- SRM objectives
- Typical SRM challenges
- Current maturity level
- Unique supplier capabilities
- Critical success factors
- Potential benefits
2. Towards world-class SRM
This chapter presents typical best practices to successfully establish and enhance
an SRM programme or to develop and manage partnerships. We will use the seven enablers from the Procurement Framework of PwC which are:
- Strategy & Governance: what does your organisation want to achieve with SRM and how are these objectives secured?
- Process: which activities does your organisation perform and how is SRM supported by a standard toolkit?
- Structure: how does your organisation structure SRM and which roles & responsibilities are established?
- People: which unique competencies does your organisation need to establish and manage SRM?
- Technology: which support systems does your organisation deploy?
- Performance Management: how does your organisation measure and improve partnership performance?
- Risk Management: how does your organisation identify and mitigate risks at key suppliers?
This chapter concludes with a short description of four key capabilities that, in our view, drive SRM value creation.
3. How to establish SRM
……
Xem và tải tài liệu ở đây
Quote from bsdinsight on 9 December 2023, 04:19Tóm tắc tài liệu như sau
🌏 Asia Pacific Growth:
- Asia Pacific is a key driver of global growth, with the region expected to contribute to 70% of global growth over the next decade.
- The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), the world’s largest free trade agreement, further strengthens Asia Pacific’s economic position.
🔄 Repositioning Supply Chains:
- Businesses face challenges in repositioning supply chains for growth, considering competitive landscapes, next-gen technologies, and ESG integration.
- CEOs must play multifaceted roles as diplomats, crisis managers, purpose evangelists, and digitally literate leaders in this shifting environment.
🌐 Global Economic Realities:
- Economic volatility, driven by factors like inflation, energy crises, and geopolitical tensions, demands a shift from resilience to long-term growth strategies.
- Transformation across the enterprise, including supply chains, is crucial for business survival and growth.
🌍 Competitive Landscape in Supply Chain Transformation:
- Geopolitical and trade tensions prompt businesses to relocate supply chain components, intensifying the competition for new suppliers and locations.
- Traditional “lift and shift” approaches are no longer sufficient; holistic and transformational changes are necessary.
📊 CEO Perspectives:
- Supply chains significantly impact industry profitability in Asia Pacific, with CEOs investing in supply chain transformation.
- Supply chain disruption, initially seen as a risk, can be an opportunity for necessary transformation and growth.
🌐 Location Considerations:
- Alternative locations in the Indo-Pacific region offer various trade-offs in terms of workforce, infrastructure, and regulatory environments.
- Considerations include labor costs, political risk, infrastructure, and skills availability.
🧠 Talent Management:
- Attracting and retaining talent involves considerations beyond monetary compensation, including career progression, work/life balance, and cultural sensitivities.
- Businesses must adapt to different ways of working, addressing technology skills shortages through upskilling and workforce development.
🌱 Sustainable Growth Strategies:
- Winning over new suppliers involves value-adding differentiation, such as deep-tier financing, joint ventures, and investments in R&D.
- Companies should look beyond government incentives and focus on access to talent and supplier pools for successful supply chain rebalancing.
🚀 Technology’s Role:
- In response to external complexities, businesses need better forecasting and faster adaptation in their supply chains.
- Leveraging technology, particularly digitization, can create transparent and autonomous supply chain ecosystems.- 🔄 Supply Chain Risks and Challenges:
- 🌐 Many risks (trade preferences, disputes, climate, cyberwarfare) lie outside the enterprise’s internal data.
- 📉 Relying on internal data alone for demand forecasting can lead to vulnerability.
- 🛒 Example: Big retail chains faced losses due to late orders and changed customer preferences.
💡 Benefits of Technology Adoption:
- 🤖 Improved efficiency and cost reduction through technology automation.
- 🌐 Enhanced resilience with real-time visibility for risk identification and rapid response.
- 🔍 Increased transparency and traceability in the supply chain.
- 🌐 Enhanced customer experience with real-time tracking and personalized recommendations.
- 🌱 Sustainability and ESG compliance through optimized transportation and reduced waste.
🔮 Next-Generation Technologies:
- 💽 Cloud-based common data platforms lead in adoption and investment.
- 🌐 Internet of Things (IoT) and connected devices show significant adoption.
- 📊 Artificial intelligence/machine learning and blockchain gaining traction.
- 🔄 Adoption and investment levels vary across technologies.
📊 Technology Adoption Trends:
- 📈 AI and machine learning lead in C-suite spending, with 22% planning at least $5mn investment.
- 📊 Survey reveals the adoption and investment levels in various technologies.
🌐 Data for Risk Management:
- 🌐 Businesses gather diverse data types for risk management (cybersecurity, operational, market, etc.).
- 📊 Source: PwC’s Global Risk Survey 2023.
📈 Digital Supply Chain Excellence:
- 🚀 Investing in advanced supply chain capabilities yields lower costs, increased revenues, and better risk management.
- 💻 Digital champions achieve significant savings and revenue increase in 22 months.
🌍 ESG and Sustainability:
- 🌱 Assessing and managing environmental footprint, social responsibility, and governance.
- 🔄 Turning ESG into a value driver for business growth.
- 🌐 Top ESG challenges include varying standards and coordinating with suppliers.
🔄 Global CEO Survey Insights:
- 🌍 Climate impact on supply chain decisions is underestimated globally but more acknowledged in Asia Pacific.
- 📊 20% of Asia Pacific CEOs believe climate risk will significantly impact supply chains.
🌐 Regulatory Landscape for ESG:
- 📜 Growing regulatory environment on ESG issues globally.
- 🚦 EU’s Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive introduces mandatory reporting from 2024-2028.
🔄 Key Takeaways:
- 🚀 Align technology adoption with overall business strategy for long-term growth.
- 🌐 AI-enabled control towers and digital twins offer real-time insights for decision-makers.
- 💬 Continuous innovation is crucial for fortifying supply chains in the evolving global reality.
🌏 Circular Economy Policies:
- Japan, China, Vietnam, and Indonesia have national circular economy policies/strategies.
- Neighboring nations in the Asia Pacific region are developing sector-specific resource-efficiency circular policies.
📉 Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM):
- The EU’s CBAM, a carbon tariff on carbon-intensive products, starts in 2026 with reporting requirements beginning earlier.
- Many exporters in Asia Pacific are unprepared for the additional import charges.
♻️ Evolution of Supply Chains:
- The definition of supply chains is evolving.
- Addressing Scope 3 emissions, especially upstream and downstream activities, is crucial for a company’s overall carbon footprint.
🌐 Human Rights in Supply Chains:
- Businesses in the Asia Pacific need to analyze and manage modern slavery and human rights risks.
- Climate impacts and adaptation risks in key export locations have implications for workers and supply chains.
🌿 ESG Integration:
- Sustainability is a driver of value, not just a cost.
- Embedding ESG principles attracts stakeholders, enhances reputation, and can lead to increased brand loyalty and investor confidence.
💼 Steps for Supply Chain Rebalancing:
- Elevate supply chain importance to the C-Suite for strategic management.
- Differentiate value propositions for potential suppliers, sites, and talent pools.
- Look beyond government incentives and invest in technology for long-term growth.
- Make ESG a value driver for growth by embedding it in the overall supply chain strategy.
- Proactively partner with suppliers to boost innovation and reduce risk.
- Businesses in Asia Pacific must adapt to global supply chain challenges for sustained growth.
📈 ESG Growth in Asia Pacific:
- Asia Pacific has the fastest percentage growth in ESG Assets-under-Management, forecasted to triple by 2026.
- Most institutional investors report higher performance yields from ESG investing and are willing to pay higher fees for ESG funds.
Tóm tắc tài liệu như sau
-
🌏 Asia Pacific Growth:
- Asia Pacific is a key driver of global growth, with the region expected to contribute to 70% of global growth over the next decade.
- The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), the world’s largest free trade agreement, further strengthens Asia Pacific’s economic position.
-
🔄 Repositioning Supply Chains:
- Businesses face challenges in repositioning supply chains for growth, considering competitive landscapes, next-gen technologies, and ESG integration.
- CEOs must play multifaceted roles as diplomats, crisis managers, purpose evangelists, and digitally literate leaders in this shifting environment.
-
🌐 Global Economic Realities:
- Economic volatility, driven by factors like inflation, energy crises, and geopolitical tensions, demands a shift from resilience to long-term growth strategies.
- Transformation across the enterprise, including supply chains, is crucial for business survival and growth.
-
🌍 Competitive Landscape in Supply Chain Transformation:
- Geopolitical and trade tensions prompt businesses to relocate supply chain components, intensifying the competition for new suppliers and locations.
- Traditional “lift and shift” approaches are no longer sufficient; holistic and transformational changes are necessary.
-
📊 CEO Perspectives:
- Supply chains significantly impact industry profitability in Asia Pacific, with CEOs investing in supply chain transformation.
- Supply chain disruption, initially seen as a risk, can be an opportunity for necessary transformation and growth.
-
🌐 Location Considerations:
- Alternative locations in the Indo-Pacific region offer various trade-offs in terms of workforce, infrastructure, and regulatory environments.
- Considerations include labor costs, political risk, infrastructure, and skills availability.
-
🧠 Talent Management:
- Attracting and retaining talent involves considerations beyond monetary compensation, including career progression, work/life balance, and cultural sensitivities.
- Businesses must adapt to different ways of working, addressing technology skills shortages through upskilling and workforce development.
-
🌱 Sustainable Growth Strategies:
- Winning over new suppliers involves value-adding differentiation, such as deep-tier financing, joint ventures, and investments in R&D.
- Companies should look beyond government incentives and focus on access to talent and supplier pools for successful supply chain rebalancing.
-
🚀 Technology’s Role:
- In response to external complexities, businesses need better forecasting and faster adaptation in their supply chains.
- Leveraging technology, particularly digitization, can create transparent and autonomous supply chain ecosystems.- 🔄 Supply Chain Risks and Challenges:
- 🌐 Many risks (trade preferences, disputes, climate, cyberwarfare) lie outside the enterprise’s internal data.
- 📉 Relying on internal data alone for demand forecasting can lead to vulnerability.
- 🛒 Example: Big retail chains faced losses due to late orders and changed customer preferences.
-
💡 Benefits of Technology Adoption:
- 🤖 Improved efficiency and cost reduction through technology automation.
- 🌐 Enhanced resilience with real-time visibility for risk identification and rapid response.
- 🔍 Increased transparency and traceability in the supply chain.
- 🌐 Enhanced customer experience with real-time tracking and personalized recommendations.
- 🌱 Sustainability and ESG compliance through optimized transportation and reduced waste.
-
🔮 Next-Generation Technologies:
- 💽 Cloud-based common data platforms lead in adoption and investment.
- 🌐 Internet of Things (IoT) and connected devices show significant adoption.
- 📊 Artificial intelligence/machine learning and blockchain gaining traction.
- 🔄 Adoption and investment levels vary across technologies.
-
📊 Technology Adoption Trends:
- 📈 AI and machine learning lead in C-suite spending, with 22% planning at least $5mn investment.
- 📊 Survey reveals the adoption and investment levels in various technologies.
-
🌐 Data for Risk Management:
- 🌐 Businesses gather diverse data types for risk management (cybersecurity, operational, market, etc.).
- 📊 Source: PwC’s Global Risk Survey 2023.
-
📈 Digital Supply Chain Excellence:
- 🚀 Investing in advanced supply chain capabilities yields lower costs, increased revenues, and better risk management.
- 💻 Digital champions achieve significant savings and revenue increase in 22 months.
-
🌍 ESG and Sustainability:
- 🌱 Assessing and managing environmental footprint, social responsibility, and governance.
- 🔄 Turning ESG into a value driver for business growth.
- 🌐 Top ESG challenges include varying standards and coordinating with suppliers.
-
🔄 Global CEO Survey Insights:
- 🌍 Climate impact on supply chain decisions is underestimated globally but more acknowledged in Asia Pacific.
- 📊 20% of Asia Pacific CEOs believe climate risk will significantly impact supply chains.
-
🌐 Regulatory Landscape for ESG:
- 📜 Growing regulatory environment on ESG issues globally.
- 🚦 EU’s Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive introduces mandatory reporting from 2024-2028.
-
🔄 Key Takeaways:
- 🚀 Align technology adoption with overall business strategy for long-term growth.
- 🌐 AI-enabled control towers and digital twins offer real-time insights for decision-makers.
- 💬 Continuous innovation is crucial for fortifying supply chains in the evolving global reality.
-
🌏 Circular Economy Policies:
- Japan, China, Vietnam, and Indonesia have national circular economy policies/strategies.
- Neighboring nations in the Asia Pacific region are developing sector-specific resource-efficiency circular policies.
-
📉 Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM):
- The EU’s CBAM, a carbon tariff on carbon-intensive products, starts in 2026 with reporting requirements beginning earlier.
- Many exporters in Asia Pacific are unprepared for the additional import charges.
-
♻️ Evolution of Supply Chains:
- The definition of supply chains is evolving.
- Addressing Scope 3 emissions, especially upstream and downstream activities, is crucial for a company’s overall carbon footprint.
-
🌐 Human Rights in Supply Chains:
- Businesses in the Asia Pacific need to analyze and manage modern slavery and human rights risks.
- Climate impacts and adaptation risks in key export locations have implications for workers and supply chains.
-
🌿 ESG Integration:
- Sustainability is a driver of value, not just a cost.
- Embedding ESG principles attracts stakeholders, enhances reputation, and can lead to increased brand loyalty and investor confidence.
-
💼 Steps for Supply Chain Rebalancing:
- Elevate supply chain importance to the C-Suite for strategic management.
- Differentiate value propositions for potential suppliers, sites, and talent pools.
- Look beyond government incentives and invest in technology for long-term growth.
- Make ESG a value driver for growth by embedding it in the overall supply chain strategy.
- Proactively partner with suppliers to boost innovation and reduce risk.
- Businesses in Asia Pacific must adapt to global supply chain challenges for sustained growth.
-
📈 ESG Growth in Asia Pacific:
- Asia Pacific has the fastest percentage growth in ESG Assets-under-Management, forecasted to triple by 2026.
- Most institutional investors report higher performance yields from ESG investing and are willing to pay higher fees for ESG funds.